Dr. Himani Pandey, BAMS
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is an essential water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. It is involved in red blood cell formation, neurological health, DNA synthesis, and energy production. Unfortunately, many people worldwide suffer from vitamin B12 deficiency, often without even realizing it. This deficiency can lead to various health issues, and early detection is vital to prevent long-term complications. In this article, we will delve into the top ten signs that may indicate a deficiency of vitamin B12.
1. Fatigue and Weakness:
One of the earliest signs of vitamin B12 deficiency is fatigue and weakness. As this vitamin is integral in energy production, low levels can result in a persistent feeling of tiredness and reduced stamina. Individuals may find it challenging to carry out routine tasks or engage in physical activities they once found easy.

2. Anemia:
Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to a specific type of anemia called megaloblastic anemia. In this condition, the body produces larger, immature red blood cells that are unable to function effectively. Anemia can manifest as paleness, dizziness, shortness of breath, and a rapid heart rate.
3. Numbness and Tingling:
Nerve damage is a common consequence of prolonged B12 deficiency, leading to a condition called peripheral neuropathy. People experiencing peripheral neuropathy may encounter sensations of numbness, tingling, or a “pins and needles” feeling, especially in their hands and feet.

4. Cognitive Impairment:
Vitamin B12 is essential for maintaining healthy neurological function. A deficiency can lead to cognitive impairment, including memory lapses, difficulty concentrating, and brain fog. In severe cases, it may even contribute to mood disorders and depression.
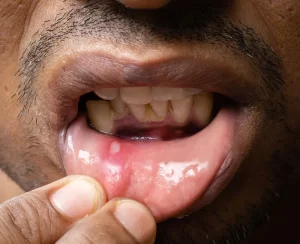
5. Glossitis and Mouth Ulcers:
Glossitis, the inflammation of the tongue, is another potential sign of vitamin B12 deficiency. A person may experience a swollen, red, and sometimes painful tongue. Additionally, the deficiency can cause mouth ulcers and a burning sensation in the mouth.
6. Digestive Issues:
Vitamin B12 absorption occurs primarily in the small intestine. Various gastrointestinal conditions, such as Crohn’s disease or celiac disease, can hinder B12 absorption and lead to deficiency. Therefore, experiencing unexplained digestive problems might warrant an investigation into B12 levels.
7. Vision Problems:
Vision disturbances may arise due to vitamin B12 deficiency affecting the optic nerve and the nervous system. Blurred or double vision and sensitivity to light are possible symptoms.

8. Pale or Jaundiced Skin:
In addition to megaloblastic anemia, B12 deficiency can cause changes in the skin, making it appear paler than usual. In severe cases, some individuals may develop a slight yellowing of the skin, known as jaundice.
9. Balance Issues and Ataxia:
Neurological symptoms may include problems with balance and coordination, known as ataxia. Affected individuals may have difficulty walking steadily and experience a greater risk of falls.
10. Infertility and Pregnancy Complications:
Vitamin B12 deficiency can affect fertility in both men and women. In pregnant women, it may lead to complications such as neural tube defects in the developing fetus.
Vitamin B12 is a vital nutrient essential for various bodily functions. Recognizing the signs of deficiency is crucial for early intervention and treatment. If you experience any of these symptoms or suspect a deficiency, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional who can perform the necessary tests and recommend appropriate supplements or dietary changes to restore optimal B12 levels and maintain overall health. Remember, prevention and awareness are the keys to a healthier life.
Image Source : Google